Road signs
 Saved road signs
Saved road signs
 Overview
Overview
 Important road signs
Important road signs
 Warning signs
Warning signs
 Priority signs
Priority signs
 Prohibitory signs
Prohibitory signs
 Mandatory signs
Mandatory signs
 Advisory signs
Advisory signs
 Direction signs for road guidance
Direction signs for road guidance
 Direction signs for pedestrians and cyclists
Direction signs for pedestrians and cyclists
 Direction signs for public institutions
Direction signs for public institutions
 Direction signs for service facilities
Direction signs for service facilities
 Direction signs for tourist attractions
Direction signs for tourist attractions
 Information signs
Information signs
 Symbols
Symbols
 Additional panels
Additional panels
 Traffic signals
Traffic signals
 Road markings
Road markings
 Traffic devices
Traffic devices
 Signals by police officers
Signals by police officers
 Saved road signs
Saved road signs
 Overview
Overview
 Important road signs
Important road signs
 Warning signs
Warning signs
 Priority signs
Priority signs
 Prohibitory signs
Prohibitory signs
 Mandatory signs
Mandatory signs
 Advisory signs
Advisory signs
 Direction signs for road guidance
Direction signs for road guidance
 Direction signs for pedestrians and cyclists
Direction signs for pedestrians and cyclists
 Direction signs for public institutions
Direction signs for public institutions
 Direction signs for service facilities
Direction signs for service facilities
 Direction signs for tourist attractions
Direction signs for tourist attractions
 Information signs
Information signs
 Symbols
Symbols
 Additional panels
Additional panels
 Traffic signals
Traffic signals
 Road markings
Road markings
 Traffic devices
Traffic devices
 Signals by police officers
Signals by police officers
Log
in
in
Join now

 The Licence Game
The Licence Game The Road Signs Game
The Road Signs Game Continue reading
Continue reading Introduction
Introduction The car
The car People
People The environment
The environment Driving in towns and cities
Driving in towns and cities Driving on country roads
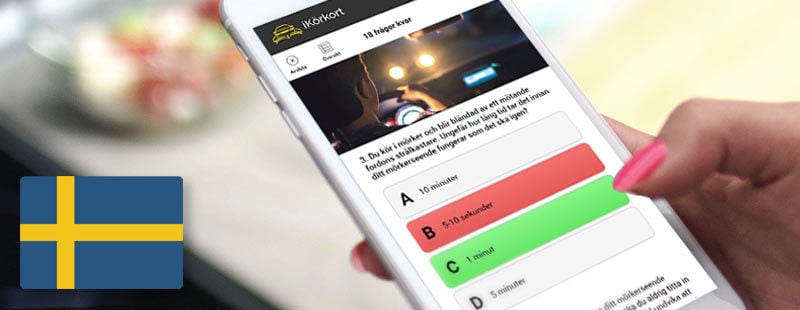
Driving on country roads Darkness and slippery conditions
Darkness and slippery conditions Accidents
Accidents Numbers and statistics
Numbers and statistics The driving test
The driving test Other
Other Audiobook
Audiobook Start free test
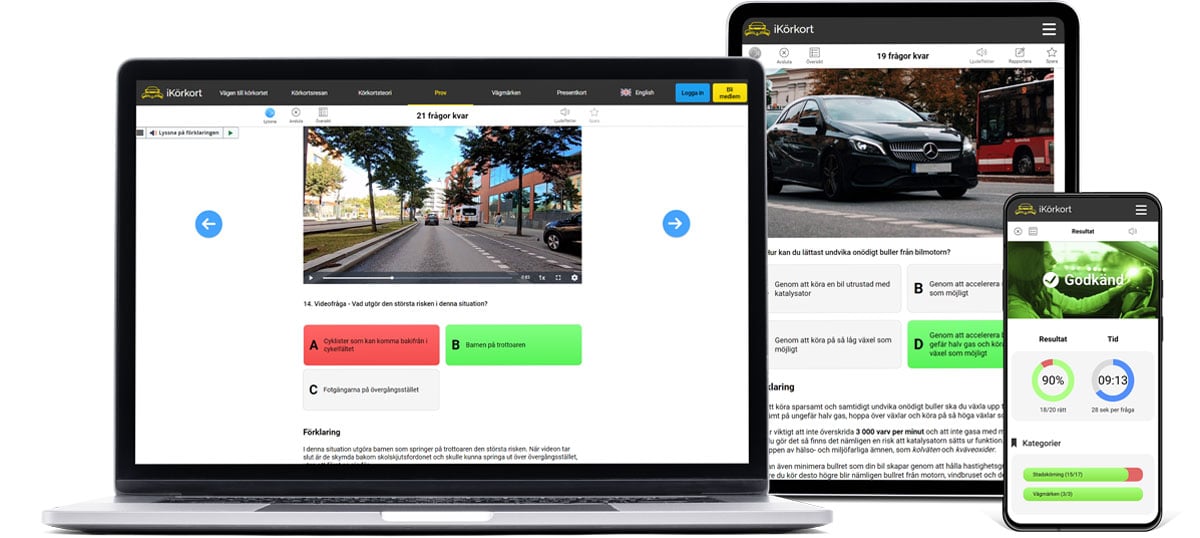
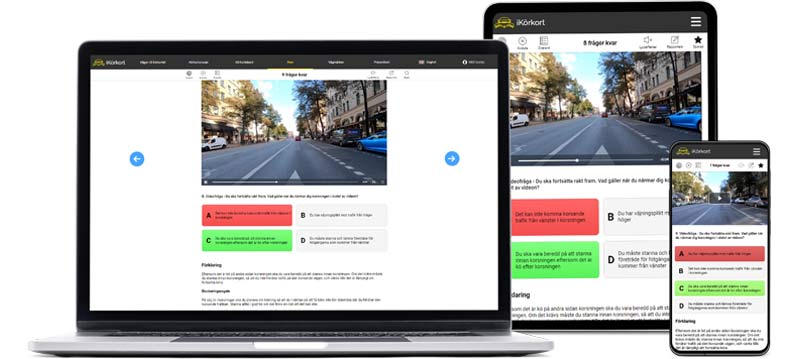
Start free test Start road signs test
Start road signs test Create custom test
Create custom test Start theory test
Start theory test Paused tests
Paused tests Completed tests
Completed tests Test statistics
Test statistics